VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION (And Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia)
Inclusion Criteria: Apneic, pulseless patients with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia treated by advanced level personnel. Basic-level personnel will use the CARDIAC ARREST Guidelines.
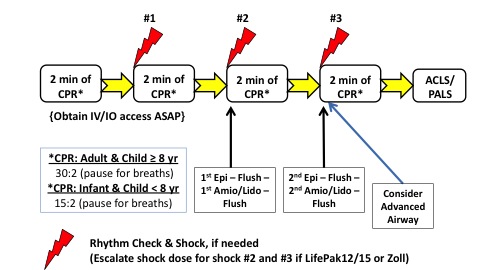
NOTE:
- Below are the energy protocols for each brand and model of manual defibrillator.
- If rescuers deliver one or more shocks to the patient prior to arrival of Advanced Level personnel, remember to increase the energy level accordingly on the manual defibrillator. In other words, do not start the shock sequence at the 1st (lowest) setting.
- DO NOT administer consecutive or back-to-back shocks.
Adult (dose in Joules)
|
1st |
2nd |
3rd & after |
LifePak12 |
200 |
300 |
360 |
LifePak 15 |
200 |
300 |
360 |
LifePak 11 |
360 |
360 |
360 |
Philips |
150 |
150 |
150 |
Zoll |
120 |
150 |
200 |
|
Pediatric (younger than 8th birthday)
- All devices:
- First shock - 2 J/kg
- Second shock – 4 J/kg
- Subsequent shocks – at least 4 J/kg (no more than 10 J/kg)
- For manual defibrillators, use pediatric defibrillation pads.
- For AEDs, use special pediatric, dose-attenuating AED pads (if available) for patients between 1st and 8th birthday.
Do not use an AED on infants under 1 year old.
NOTE: Following any countershock, do not pause to check the rhythm on the monitor. Instead, immediately resume CPR (starting with effective chest compressions) at a rate of 100-120 per minute for two minutes before the next rhythm check (or shock, if needed). Use a metronome.
- Follow the CARDIAC ARREST Guidelines for patients in cardiac arrest, with attention to maintaining high quality, uninterrupted chest compressions at all times.
- At the end of EACH two-minute period of CPR, check the ECG rhythm and pulse.
- In the event of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), refer to the POST-CARDIAC ARREST CARE Guidelines.
- If asystole or PEA develops, resume CPR and refer to the ASYSTOLE/PEA Guidelines.
- If the patient is in VF or pVT, resume chest compressions while charging the defibrillator to the appropriate energy level and deliver the FIRST, SINGLE SHOCK.
- Immediately after the shock, resume CPR for 2 full minutes.
- During this 2-minute period, apply the ETCO2 monitor and establish vascular access (if not already done), without interrupting chest compressions.
- If the patient remains in VF or pVT, resume chest compressions while charging the defibrillator to the appropriate energy level and deliver the SECOND, SINGLE SHOCK. Immediately after the second shock, resume CPR for 2 full minutes. During this 2-minute period, administer epinephrine 1:10,000 IVP or IOP with a flush, and an antiarrhythmic with a flush, as soon as possible after shock delivery, as follows:
Adult
- Epinephrine 1:10,000: 1 mg IVP or IO; flush with 20 mL Normal Saline; AND
- Amiodarone 300 mg IVP or IO; immediate flush with 20 mL Normal Saline.
- If the etiology of the arrest is trauma, administer lidocaine 1 mg/kg - 1.5 mg/kg IV/IO push, instead of amiodarone.
- If the rhythm could be Torsades de Pointes, add 2 grams magnesium sulfate to 250 mL Normal Saline & infuse IV piggyback wide open.
- BioTel authorization required if dialysis patient.
Pediatric
- Epinephrine 1:10,000: 0.01 mg/kg IVP or IO (0.1 mL/kg); flush with 10 mL Normal Saline; AND
- Amiodarone 5 mg/kg IVP or IO; immediate flush with 10 mL Normal Saline:
- Maximum single dose = 300 mg.
- If the patient remains in VF or pVT, resume chest compressions while charging the defibrillator to the appropriate energy level and deliver the THIRD, SINGLE SHOCK. Immediately after the shock, resume CPR for 2 full minutes. During this 2-minute period, administer epinephrine 1:10,000 IVP or IOP with a flush, and an antiarrhythmic drug with a flush, as soon as possible after shock delivery, as follows:
Adult
- Epinephrine 1:10,000: 1 mg IVP or IO; flush with 20 mL Normal Saline; AND
- Amiodarone 150 mg IVP or IO; immediate flush with 20 mL Normal Saline.
- If the etiology of the arrest is trauma, administer lidocaine 1 mg/kg - 1.5 mg/kg IV/IO push, instead of amiodarone.
Pediatric
- Epinephrine 1:10,000: 0.01 mg/kg IVP or IO (0.1 mL/kg); flush with 10 mL Normal Saline; AND
- Amiodarone 5 mg/kg IVP or IO; immediate flush with 10 mL Normal Saline:
- Maximum single dose = 300 mg.
- At the end of the two-minute period of CPR, check a pulse and the ECG rhythm.
- In the event of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), refer to POST CARDIAC ARREST MANAGEMENT Guidelines.
- If asystole or PEA develops, resume CPR and refer to the ASYSTOLE/PEA Guidelines.
- If the patient remains in ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, attempt defibrillation again with a SINGLE shock at the highest energy level recommended for that device, and immediately resume CPR for two minutes. Repeat this cycle if the patient either remains in VF/pVT or at any time returns to these rhythms.
- Consider placement of an advanced airway.
- NOTE: The 2nd dose of amiodarone may be administered at any subsequent rhythm check after the first interval of CPR, as needed, for recurrent or persistent VF/pVT. Do NOT administer more than 2 total doses of amiodarone. Do NOT administer additional doses of amiodarone or lidocaine, either during the resuscitation, or after ROSC has been achieved, unless authorized by BioTel (rarely, if ever, indicated). Epinephrine may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes after the first dose, as needed.
- If any of these possible causes of VF/pVT is suspected, initiate standing order treatment ASAP:
Hyperkalemia (renal failure or dialysis) or pre-existing acidosis (e.g. renal failure, dialysis, methanol ingestion, aspirin overdose) or tricyclic antidepressant overdose
Adult and Pediatric
- Sodium bicarbonate 1 mEq/kg IVP/IO; flush with at least 10 mL of Normal Saline.
If mechanism of injury AND symptoms AND physical exam suggest a tension pneumothorax:
Adult
- Perform needle thoracostomy.
Pediatric
- Perform needle thoracostomy.
- Contact BioTel as soon as possible.
If beta blocker toxicity, administer:
Adult
- Glucagon 1 mg – 2 mg IVP/IO Push.
- May repeat once after 20 minutes.
Pediatric
- Glucagon 0.5 mg (under age 1 yr) or 1 mg (at least one year of age) IV/IO, IM, or IN.
- May repeat once after 20 minutes.
If calcium channel blocker toxicity, administer
Adult
- Calcium chloride (10% solution) 10 – 15 mg/kg IVP/IO Push. (optional medication)
Pediatric
- Contact BioTel for authorization and dosing (risk of phlebitis). (optional medication)
- If the resuscitation attempt is prolonged (greater than 15 minutes), consider [not required]:
Adult
- Sodium bicarbonate 1 mEq/kg IV/IO Push, and/or
- Calcium chloride (10% solution) 10 – 15 mg/kg IV/IO Push (0.1 – 0.15 mL/kg). (optional medication)
Pediatric
- Sodium bicarbonate 1 mEq/kg IVP/IO Push.

